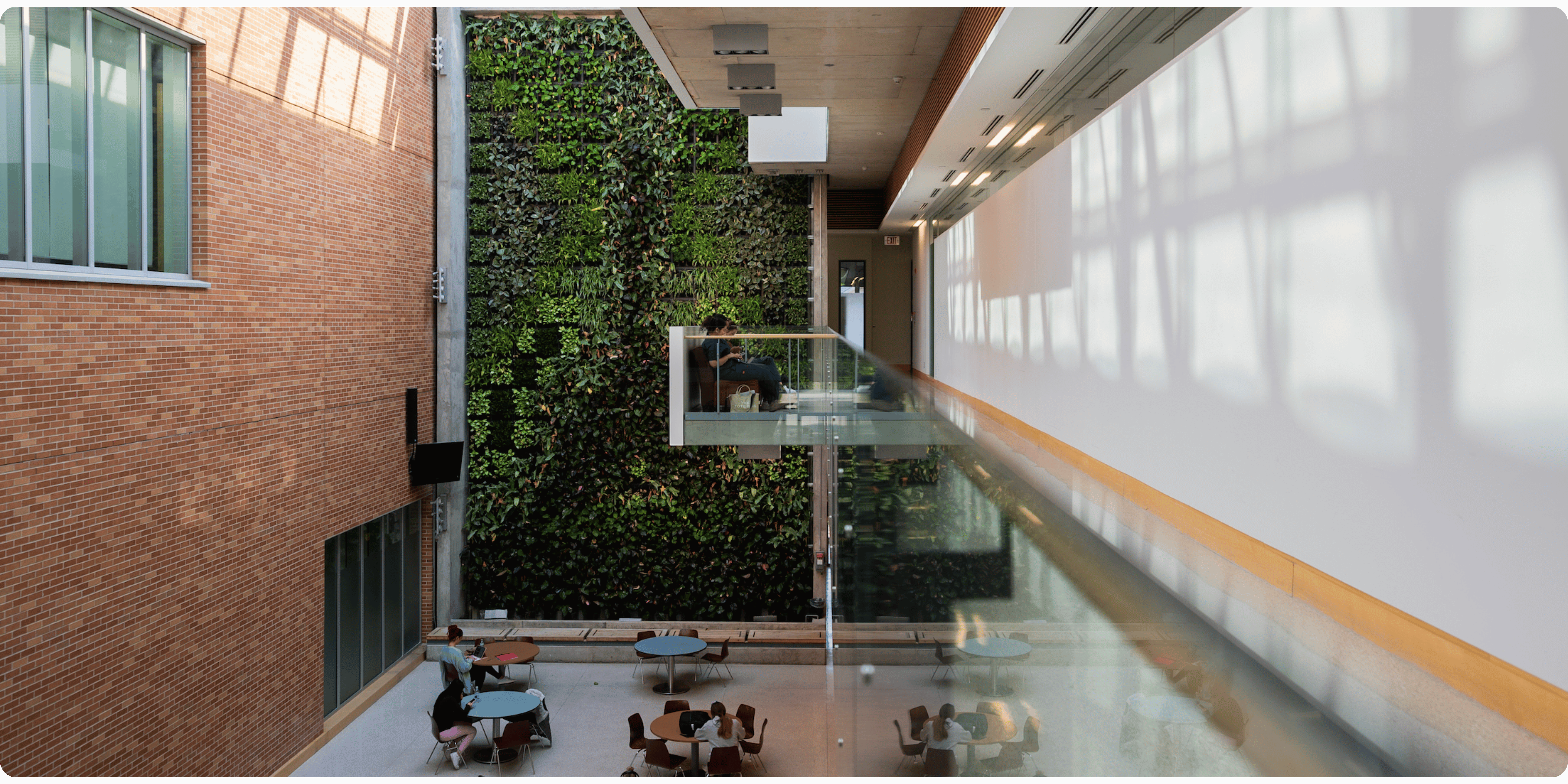
Educational institutions are increasingly recognizing the importance of sustainable development, leading to a surge in investments in green infrastructure. These sustainability initiatives not only enhance environmental stewardship but also offer economic benefits and improved learning environments. Summer breaks provide an opportune time for schools to undertake construction projects, minimizing disruption to academic activities.
Why Are Educational Institutions Investing in Green Infrastructure?
Green infrastructure encompasses a range of sustainable practices, including energy-efficient buildings, renewable energy installations, water conservation systems, and the incorporation of green spaces. For educational facilities, these investments address several critical objectives:
- Environmental Responsibility: By reducing carbon footprints and promoting sustainability, schools demonstrate a commitment to environmental stewardship, fostering a culture of environmental responsibility among students.
- Economic Efficiency: Energy-efficient systems and renewable energy sources can significantly reduce utility costs, leading to long-term financial savings.
- Enhanced Learning Environments: Access to natural light, improved air quality, and green spaces have been shown to boost student performance and well-being.
What Green Infrastructure Are They Investing In?
One major focus is the construction or retrofitting of energy-efficient buildings, which incorporate advanced insulation, biofilter-integrated HVAC systems, and smart lighting controls to reduce energy consumption. In parallel, many schools are turning to renewable energy installations, such as solar panels, wind turbines, and geothermal heating and cooling systems, to further reduce reliance on fossil fuels and cut greenhouse gas emissions.
Water conservation systems are also a growing priority, with schools implementing low-flow fixtures, rainwater harvesting solutions, and drought-tolerant landscaping to significantly reduce water use.
Finally, there is a strong push to develop green spaces—including gardens, green roofs, and outdoor classrooms—that give students access to nature, support biodiversity, and serve as hands-on environmental learning tools.
Implementation Strategies and Timelines
Effective implementation of green infrastructure projects requires thoughtful and meticulous planning. Some key steps include:
- Assessment and Goal Setting: Conducting energy audits and environmental assessments to identify areas for improvement and establish clear objectives.
- Stakeholder Engagement: Involving faculty, students, parents, and the community to gather input and foster support for initiatives.
- Securing Funding: Exploring grants, partnerships, and financing options to support projects. For instance, a case study in Austria highlights funding models for low-cost, do-it-yourself greening systems in schools.
- Design and Planning: Collaborating with architects and engineers to develop detailed plans that align with sustainability goals and budget constraints.
- Construction During Summer Break: Scheduling major construction activities during summer to minimize disruption to the academic calendar.
- Monitoring and Maintenance: Establishing protocols to track performance and ensure the longevity of green infrastructure investments.
Investing in green infrastructure enables educational institutions to enhance sustainability, reduce operational costs, and create healthier learning environments. By adopting strategic planning and leveraging successful models, schools can effectively implement improvements that benefit both the environment and their academic communities.